Updated 1 week ago
How Are Solar Panels Made? A Comprehensive Overview
Written by Dan Simms Dan SimmsDan has been a solar proponent for more than a decade now, and he has been researching and writing about solar and renewable energy for the past five ...Learn more , Edited by Catherine Lane Catherine LaneCatherine has been researching and reporting on the solar industry for five years and is the Written Content Manager at SolarReviews. She leads a dyna...Learn more

Why you can trust SolarReviews
SolarReviews is the leading American website for solar panel reviews and solar panel installation companies. Our industry experts have a combined three decades of solar experience and maintain editorial independence for their reviews. No company can pay to alter the reviews or review scores shown on our site. Learn more about SolarReviews and how we make money.
Solar panels may seem like complicated pieces of equipment since they turn sunlight into usable, 100% clean energy for our homes. In reality, they're pretty simple. In this guide, we'll explain how solar panels are made, what they're made of, and where they're manufactured to give you a more holistic view of solar technology.
Key takeaways
Solar panels are manufactured using silicon, glass, and metal. Silicon creates solar cells that can generate electricity from the sun.
The main types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels. Their manufacturing process is slightly different, leading to different attributes for each type of panel.
Solar panels are manufactured all over the world. American-made solar panels are generally more expensive, but they are typically high quality.
What are solar panels made of?
Solar panels are made of four primary materials: silicon, metal, glass, and plastics. Each component has a distinct purpose:
Silicon makes up the solar cells, which are the part of the solar panel that converts sunlight into electricity.
Metals create a protective frame that protects the panel and holds it in place. Solar panel frames are usually made of aluminum.
Glass covers the silicon solar cells and protects them from the elements.
Plastic acts as a backsheet that protects the back of the panel.
Some other materials come into play, as well, like the sealants used to hold the panels together, materials within the wiring and busbars that bring the solar electricity to your home.
How are solar panels made?
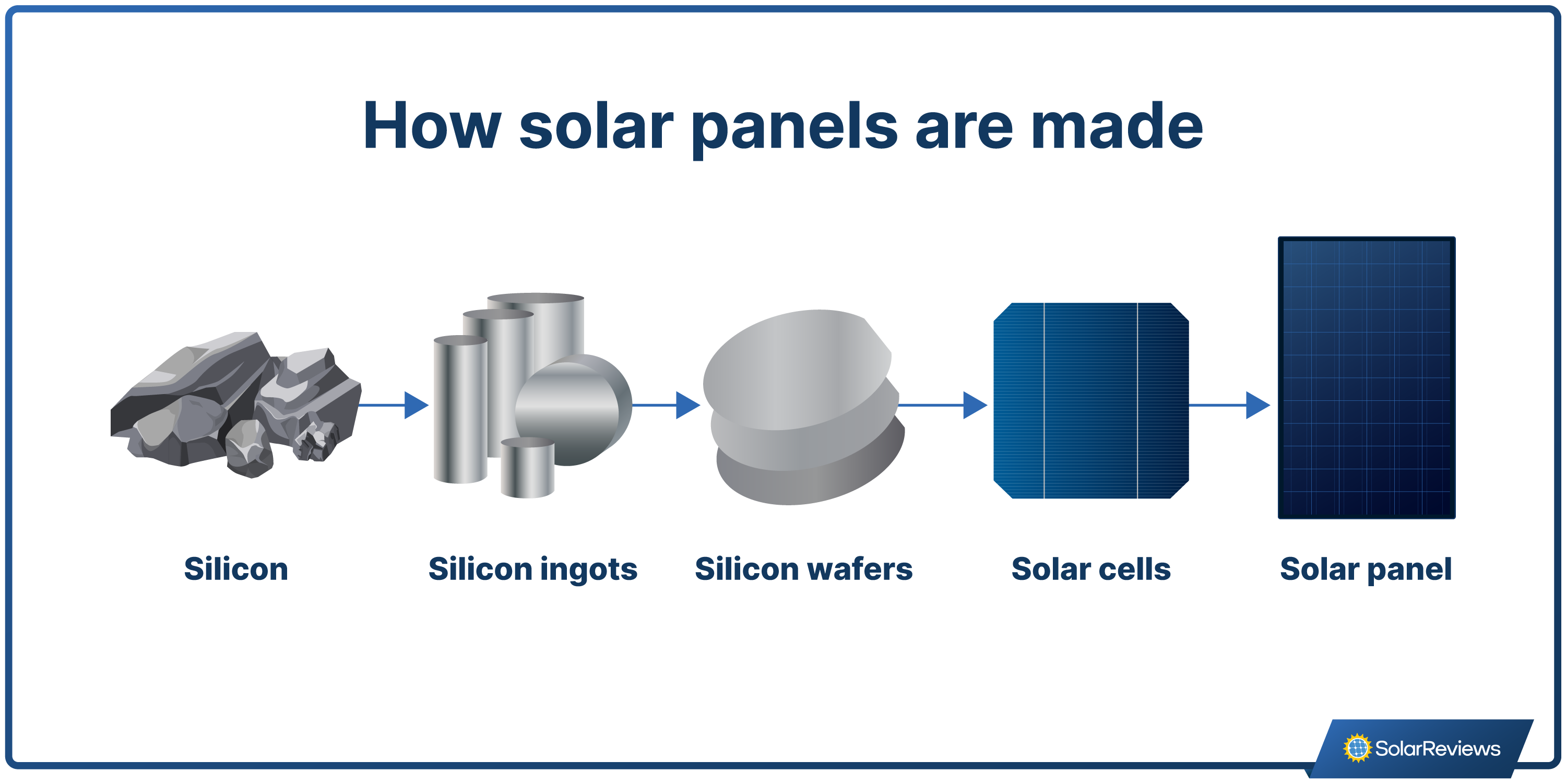
How exactly do these materials all come together to create a functioning solar panel? There are a few key steps to understand.
Step 1: Making the solar cells
The process starts with mining raw materials. Silicon comes from quartz minerals, which are mined and purified to separate the silicon. Solar cell manufacturers use high temperatures to grow a silicon ingot, which is essentially one large block of silicon that is sliced into wafers.
Silicon is a natural semiconductor, but it is usually “doped” with boron or gallium to improve performance. Phosphorus is also used to make the solar cells operate as efficiently as possible.
The solar PV cell is then coated with an anti-reflective coating, allowing more sunlight to reach the cell for increased efficiency. More sunlight means more excited electrons, which means more electricity is generated for your home. Thin lines are then cut into the cells to capture and move the electrical current within the cell.
Some solar panel brands make their own solar cells, while others purchase them from a stand-alone solar cell manufacturer.
P-type vs. n-type solar cells
P-type silicon cells are built on a positively charged base, meaning the bottom layer of the solar cell is mixed with boron and the top layer contains phosphorus.
N-type solar cells are the opposite, with the phosphorus layer serving as a base.
The main difference between these types of solar cells is that n-type solar cells are more efficient and are not affected by light-induced degradation, which means they’re more durable.
Step 2: Connecting solar cells together
Once the solar cells are made, the solar panel manufacturer will solder them together to create a sheet of cells. Most solar modules for homes have 60 cells, while commercial solar panels have 72 cells.
Step 3: Constructing the panel
Solar panels are more than just a sheet of solar cells. Once the cells are soldered together, a backsheet is added to protect the underside of the solar cells. Next, the manufacturer will encapsulate the solar cells and backing sheet under a sheet of reinforced glass and inside a metal frame for stability.
Step 4: Installing the junction box
The last step of the process includes installing the peripherals, like wiring connections and junction boxes. Junction boxes are where the internal wiring of the solar panel and the external connections meet, keeping them safe and protected from weather and other external factors.
Some solar panels, called AC-solar panels, have inverters attached to them during the manufacturing process.
Step 5: Testing the solar panels
Most manufacturers will also put the panel through rigorous testing to ensure product quality and efficiency. Any cracked or bent solar panels will be discarded, and the rest will be tested to make sure they can stand up to intense weather conditions, heat, and normal wear and tear.
They’ll also test that the electrical current travels through the panel efficiently so it can generate solar power as it should.
Where are solar panels made?
Most of the solar panels in the world are manufactured in China. According to the International Energy Agency, China accounts for almost 75% of global solar module manufacturing. Vietnam, India, Thailand, Malaysia, and the United States are also responsible for a portion of solar manufacturing.
With the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 and new tariffs introduced by the Trump Administration, there could be a boost in solar panels made in the United States.
What are the different types of solar panels?
Now that you know how solar panels are made, you can get a better understanding of the different types of solar panels and choose the one that best meets your needs when you go solar.
Monocrystalline solar panels
Monocrystalline solar panels contain solar cells that are each cut from a single silicon crystal. The uniform construction of a single silicon crystal makes for a more efficient solar panel, which means more energy production and more electric bill savings.
Monocrystalline solar panels are slightly more expensive than other types, but they generate the most electricity and are the most popular type of solar panel used for home solar.
Types of monocrystalline solar cells
Not all solar cells are manufactured the exact same way. Over time, solar panel technologies have changed, leading to a few different types of solar cells. Here are some of the most popular solar cell types:
PERC solar cells: Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact (PERC) solar cells have an additional layer that reflects back photons that aren’t absorbed initially by the solar cell, increasing efficiency and electricity production slightly. PERC cells have become quite common.
TOPCon solar cells: Tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) solar cells have a thin layer of silicon dioxide and a layer of phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon added to increase efficiency. TOPCon technology has been very popular in recent years, but there have been a number of patent lawsuits surrounding it.
HJT solar cells: Heterojunction (HJT) solar cells combine solid silicon wafers with thin-film solar technology, allowing the cells to absorb more sunlight. Panasonic solar panels are a popular brand that utilizes HJT cells.
Polycrystalline solar panels
Polycrystalline solar panels use solar cells that are made from fragments of multiple silicon crystals. The fragments are melted together, which makes for a simpler and more affordable manufacturing process, but they don’t produce electricity as efficiently as monocrystalline solar cells.
Manufacturing processes of monocrystalline solar cells have also become cheaper as the technology is more widely used, making the price difference between poly and mono solar cells almost negligible.
You will almost never get a home solar quote using polycrystalline solar panels.
Thin-film solar panels
Thin-film solar panels don’t use rigid silicon crystals and instead make use of doped metal oxides called transparent conductive oxides (TCOs). These sheets absorb sunlight similarly to silicon wafers, but they’re flexible.
Thin-film panels have lower efficiency ratings than most monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, but they’re flexible and allow for installation over a variety of surfaces, like curved RV roofs.
Should you make your own solar panels?
We do not recommend making your own solar panels, although it might seem easy to configure a panel with all of the proper materials. Errors in building your own panels, like starting a fire, outweigh the benefits of DIY solar panels.
It is best to rely on professionally built solar technology because they are built with rigorous standards and tested for durability. Finding the best solar panel company for your needs is is an important step to making sure your solar panels are made with high-quality materials that will provide solar power for their 25-year warranty, or more. Renewable energy from solar panels is one of the best electricity sources for reducing carbon dioxide from fossil fuels, so adding them to your home is a great way to be part of the clean energy future.
Dan has been a solar proponent for more than a decade now, and he has been researching and writing about solar and renewable energy for the past five years. He has first-hand experience with solar conversion, and he uses that and his research to help homeowners lower their electric bills and reduce their carbon footprint through solar education and adoption. He has written for major publications, including CNN, USA Today, and EcoWatch, and he has...
Learn more about Dan Simms