Updated 2 months ago
How Many Solar Panels Do I Need? 4 Step Solar Calculator Guide
Written by Catherine Lane Catherine LaneCatherine has been researching and reporting on the solar industry for five years and is the Written Content Manager at SolarReviews. She leads a dyna...Learn more
Find out how many solar panels you need based on recent installations in your area

Why you can trust SolarReviews
SolarReviews is the leading American website for solar panel reviews and solar panel installation companies. Our industry experts have a combined three decades of solar experience and maintain editorial independence for their reviews. No company can pay to alter the reviews or review scores shown on our site. Learn more about SolarReviews and how we make money.
Key takeaways
The average home needs between 15 and 19 solar panels to cover its daily electric usage.
The formula for calculating how many solar panels you need = (Monthly energy usage ÷ Monthly peak sun hours) ÷ Solar panel output
You can use annual energy use for a more accurate estimate of how many solar panels your house needs.
Your electric bils, sun exposure, roof space and design, home size, utility regulations, and budget can all impact how many solar panels you install.
Most homeowners need 15 to 19 solar panels to meet their power needs. Understanding how many solar panels your home needs helps you evaluate solar quotes effectively so you can maximize your energy production and bill savings without sacrificing your budget.
But how exactly do you calculate the right number of panels for your home? Our home solar experts put together a step-by-step solar calculator guide to help you answer the age-old question, “How many solar panels do I need?”.
Solar system sizing guide: how many solar panels do you need?
Home Size | Estimated monthly electric bill | Number of solar panels needed | Estimated roof space needed | Estimated solar cost after incentives |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1,000 sq. feet | $77 | 8 | 141 sq. feet | $6,537 |
1,500 sq. feet | $115 | 12 | 211 sq. feet | $9,806 |
2,000 sq. feet | $153 | 15 | 264 sq. feet | $13,075 |
2,500 sq. feet | $191 | 19 | 334 sq. feet | $16,343 |
3,000 sq. feet | $230 | 23 | 405 sq. feet | $19,612 |
Estimates assumed 146 monthly peak sun hours, 400-watt solar panels, and a $0.17/kWh electric rate.
How many solar panels you need varies with multiple factors, like where you live, the design of your roof, and energy consumption. To find out how much solar your specific home needs, use this solar calculator, which considers your personal energy usage and local rates to give you a personalized estimate.
Step-by-step guide: how to calculate how many solar panels you need
You can get an estimate of how many solar panels you need by using the following formula:
(Monthly energy usage (kWh) ÷ Monthly peak sun hours) ÷ Solar panel output (kW)
4 steps for calculating how many solar panels you need:
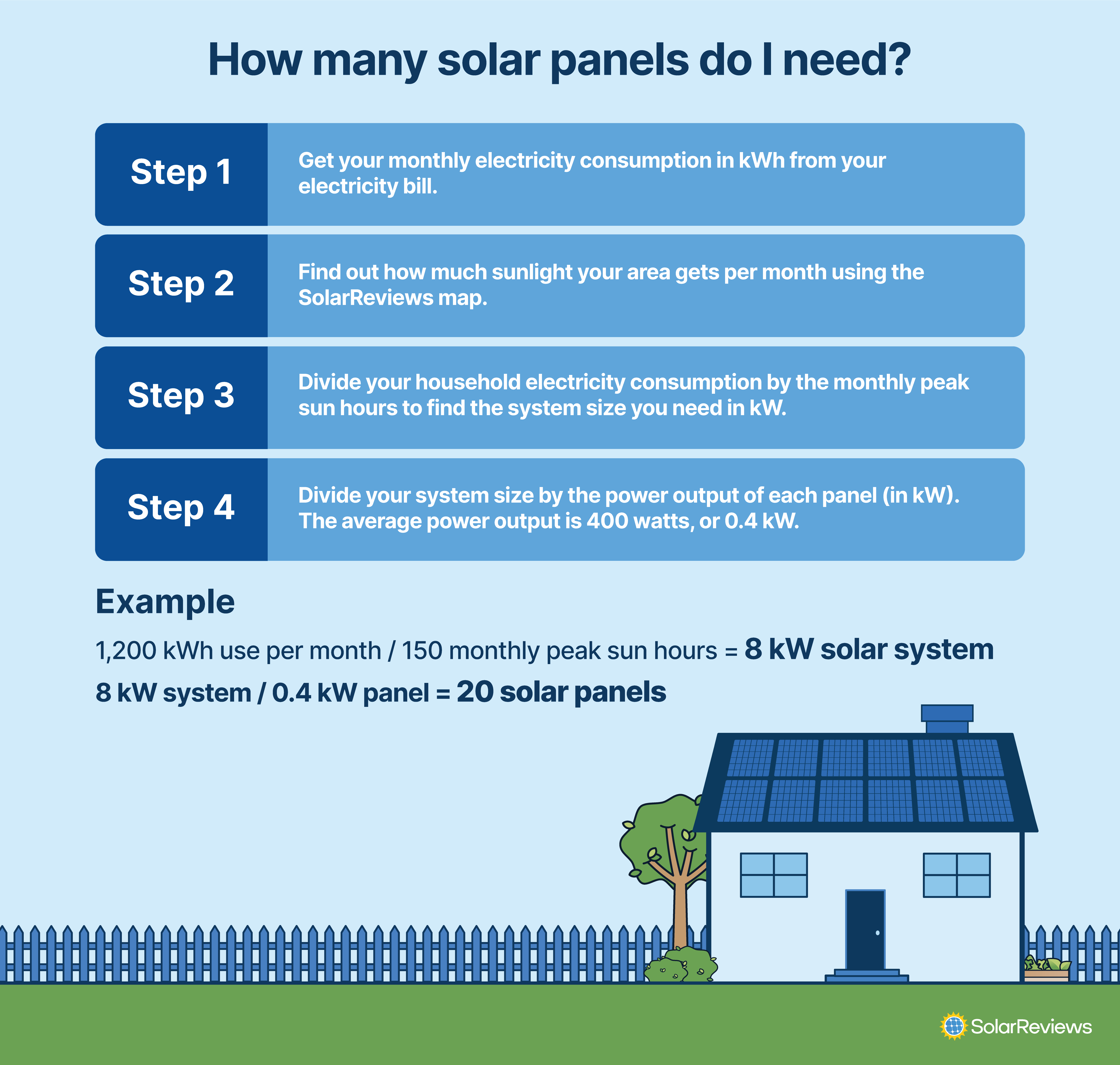
Step 1: Find your monthly electricity usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
You can find this at the bottom of your electricity bill. The average home’s energy usage is about 900 kWh per month, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Step 2: Determine how much sunlight your home gets per month, measured in peak sun hours.
Peak sun hours represent the intensity of the sun in your area, with the average home receiving about 137 peak sun hours per month.
Step 3: Divide your household electricity consumption by the monthly peak sun hours.
This calculation gives you the size of the system you need to install to cover your energy needs in kilowatts (kW). The solar quotes you get from installers will list the system size in kW.
Step 4: Divide the system size by the power output of the solar panels being used and get the number of solar panels you need.
This calculation tells you how many solar panels you will need to run your home. Most solar panels today have a power output rating of 400 watts, or 0.4 kW. Make sure you divide the system size by the panel wattage in kilowatts.
It's that easy! By using these four steps, you can estimate how many solar panels your home needs, so you'll be prepared when you talk to solar installers!
Example: Calculating how many solar panels you need to power a home
Mr. Exampleson lives in sunny Florida and wants to install solar panels to lower his high electric bills so he can put that money toward retirement instead. He read his electricity bill and saw that he used 1,200 kWh of electricity last month, which cost him $168!
He found that his home receives about 160 peak sun hours each month using the SolarReviews peak sun hour map. By dividing his energy usage and sun exposure, Mr. Exampleson figured out what size solar system is needed to cover all of his electric needs.
1,200 kWh ÷ 160 monthly peak sun hours = 7.5 kW
By researching, Mr. Exampleson discovered that the average solar panel usually has a power output rating of 400 watts, equal to 0.4 kW. Dividing the 7.5 kW solar panel system size from earlier by 0.4 kW per solar panel told him how many solar panels he needed.
7.5 kW system size ÷ 0.4 kW per panel = 19 solar panels
So, Mr. Exampleson can install 19 solar panels to lower his $168 in electric costs to $0!
Factors that determine how many solar panels you need
Every home is unique, and so is every solar installation! Several factors influence the number of solar panels you need to install, including your electric bills, roof design, and the solar panels you choose.
Electric bills
The amount of electricity you use has the biggest impact on how many solar panels you need. If you use a lot of electricity, you’ll need a lot of solar panels!
Energy consumption can vary based on:
The size of your family
Your home’s energy efficiency
The types of appliances you use
The state you live in
The table below outlines how many solar panels you need based on different energy usage levels:
Monthly energy consumption | Number of solar panels needed |
|---|---|
800 kWh | 14 |
1,000 kWh | 17 |
1,200 kWh | 21 |
1,400 kWh | 24 |
1,600 kWh | 27 |
1,800 kWh | 31 |
2,000 kWh | 34 |
Assumes 400 W panels
For example, a home with an electric stove, water heater, and clothes dryer will have a higher electricity bill than one with gas appliances. Your home’s electric consumption will be listed in kilowatt-hours (kWh) at the bottom of your electricity bill.
Sun exposure
Solar panels rely on sunlight to generate electricity. Homes in sunnier places can install fewer solar panels to cover their electricity bills. For example, one 400-watt solar panel in Arizona can produce almost 90 kWh of electricity in one month. That same panel could only generate 36 kWh in Alaska.
How much sunlight your home receives is measured in peak sun hours. The map below outlines how many peak sun hours each state receives in an average month.

Location | Daily Peak Sun Hours (PSH) | Monthly Peak Sun Hours | Average solar panel monthly energy production (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
Alabama | 4.5 – 5.4 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Alaska | 1.2 – 3 | 90 | 36 kWh |
Arizona | 7 – 8 | 222 | 88.8 kWh |
Arkansas | 4.5 – 5.4 | 132 | 52.8 kWh |
California | 5 – 7.5 | 192 | 76.8 kWh |
Colorado | 5 – 7 | 180 | 72 kWh |
Connecticut | 4.5 – 4.9 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Delaware | 4.5 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Florida | 5 – 5.9 | 162 | 64.8 kWh |
Georgia | 4.5 – 5.4 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Hawaii | 4 – 7.5 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Idaho | 4 – 6 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Illinois | 4.2 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Indiana | 4.0 – 4.4 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Iowa | 4.0 – 4.4 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Kansas | 5.0 – 6.4 | 165 | 66 kWh |
Kentucky | 4.0 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Louisiana | 4.5 – 5.4 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Maine | 4.0 – 4.4 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Maryland | 4.5 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Massachusetts | 4.5 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Michigan | 4.0 – 4.4 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Minnesota | 4.2 – 4.6 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Mississippi | 4.5 – 5.4 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Missouri | 4.5 – 5.4 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Montana | 4.5 – 5.4 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Nebraska | 5.0 – 5.9 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Nevada | 6 – 7.5 | 210 | 84 kWh |
New Hampshire | 4 – 4.5 | 120 | 48 kWh |
New Jersey | 4 – 4.5 | 135 | 54 kWh |
New Mexico | 6 – 7.5 | 210 | 84 kWh |
New York | 4 – 4.5 | 120 | 48 kWh |
North Carolina | 4.5 – 5.4 | 135 | 54 kWh |
North Dakota | 4.5 – 5.4 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Ohio | 4.0 – 4.4 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Oklahoma | 5.0 – 6.4 | 165 | 66 kWh |
Oregon | 3.5 – 6.4 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Pennsylvania | 4.0 – 4.9 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Rhode Island | 4.5 – 4.9 | 120 | 48 kWh |
South Carolina | 4.5 – 5.4 | 150 | 60 kWh |
South Dakota | 4.5 – 5.9 | 150 | 60 kWh |
Tennessee | 4.5 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Texas | 4.0 – 7.5 | 180 | 72 kWh |
Utah | 5.0 – 7.4 | 195 | 78 kWh |
Vermont | 4.0 – 4.4 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Virginia | 4.0 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Washington | 2.5 – 5 | 135 | 54 kWh |
West Virginia | 4.0 – 4.4 | 120 | 48 kWh |
Wisconsin | 4.0 – 4.9 | 135 | 54 kWh |
Wyoming | 4.5 – 6.4 | 165 | 66 kWh |
Roof orientation
South-facing roofs with an angle of 30 to 45 degrees are ideal for maximum solar energy production. Solar panels can still be installed if your roof faces another direction, but you might need a few extra panels to generate how much power you need.
Solar panels used
Not all solar panels are the same, so the ones you choose will impact how many you need to install. A solar panel’s output has the biggest impact on how much energy it produces. An average 400-watt monocrystalline solar panel will produce 2 kWh of energy per day. Solar panels with higher efficiency ratings will generally have higher wattages and are best for homes with limited roof space. The table below outlines how much energy different types of solar panels produce per month:
Panel wattage | Panels needed for average electric usage |
|---|---|
250 watts | 26 |
300 watts | 22 |
350 watts | 19 |
400 watts | 17 |
450 watts | 15 |
Assumes 137 monthly peak sun hours.
Home size
Although the square footage of your home isn’t the most accurate way to calculate how many solar panels you need, it can give you a general idea as you start your solar journey. The table below shows how many solar panels different-sized homes need on average:
Square footage | Number of 400 W solar panels needed |
|---|---|
1,000 | 8 |
1,500 | 12 |
2,000 | 16 |
2,500 | 20 |
3,000 | 24 |
Why SolarReviews doesn’t use production ratio. You may have come across the idea of a production ratio on other websites. A solar production ratio assumes that you know the amount of energy a solar system generates and the total wattage of the system. Our formula doesn’t require you to have any specific details about the solar installation you’re trying to calculate for - it’s all based on information about your home and location.
4 things that can limit how many solar panels you can install
Sometimes, you won’t be able to install all of the solar panels you need. Here are a few limiting factors that impact the number of solar panels that you can get.
1. Roof size and design
A typical 7.6 kW solar installation has an area of about 334 square feet, about 20% of the space of an average residential roof. If you have space constraints, consider high-efficiency panels that can produce more electricity in less space.
Solar panels can’t be installed where there are obstructions on your roof, like vents, chimneys, or skylights, ultimately limiting how many solar panels you can install.
The following table outlines how much roof space is needed for different amounts of solar panels:
Number of panels | System size | Minimum roof space required |
|---|---|---|
10 | 4 kW | 177 square feet |
15 | 6 kW | 265 square feet |
20 | 8 kW | 353 square feet |
25 | 10 kW | 442 square feet |
30 | 12 kW | 530 square feet |
Assumes 400 W panels
2. Shading
Shading can be an obstacle when installing solar panels. While trimming trees or bushes can help reduce shading, things like neighboring houses are harder to manage. If shading is unavoidable, you won’t be able to install solar panels on certain areas of your roof. However, you could install more solar panels elsewhere if its more suitable.
3. Utility restrictions
Every utility company bills solar customers differently, impacting the number of solar panels you should install. Some utilities don’t provide full credit for excess solar power produced beyond your monthly energy consumption, meaning you’ll want to install fewer panels to avoid overpaying for a larger system.
Many utilities also have system size limits based on energy usage, so people don’t over-install solar panels just to get extra bill savings. Most utility companies allow installations to cover up to 120% of a home’s annual energy usage, but the exact restrictions depend on the utility.
4. Personal budgets and cost
Solar panels can deliver substantial electric bill savings, but they come with a significant price tag. Solar panels cost about $3.03 per watt installed, or about $14,000 after the federal solar tax credit is considered. That's not pocket change!
If the price is too high, you can install fewer solar panels you install to better fit your budget.
How many solar panels do I need to go off-grid?
Going completely off the grid with solar panels requires you to install enough solar to cover all of your energy usage, plus a big enough battery system to power your home after the sun goes down. Off-grid solar systems are not connected to the grid at all, so it’s even more important that your solar and battery systems are properly sized.
For a monthly energy usage of 1,000 kWh, you would need at least 17 solar panels and three solar batteries to go off-grid.
Monthly energy usage | Solar panels needed | Solar batteries needed | Total system cost after tax credit |
|---|---|---|---|
500 kWh | 9 | 2 | $22,611 |
1,000 kWh | 17 | 3 | $34,373 |
1,500 kWh | 26 | 5 | $53,066 |
2,000 kWh | 34 | 6 | $66,718 |
Assumes 400-watt solar panels and 13.5 kWh lithium-ion batteries.
7 questions to ask yourself to calculate how many solar panels you need
1. How much solar power do I need?
Most homeowners aim to install enough solar panels to cover all of their electricity consumption.
Some people prefer to cover just a portion of their electricity costs, often due to budget restrictions, roof space constraints, or how their utility bills solar customers.
There are also scenarios where you might install a larger solar system, like if you plan to get an electric car, install a pool, or electrify your appliances.
You can usually find your monthly electricity usage at the bottom of your electric bill.
2. How much sunlight does my house get?
Solar panels use sunlight to generate electricity, so the more sun exposure your roof gets, the fewer solar panels you need to install.
The amount of sunlight available depends on your home’s location and climate. For example, a solar panel produces significantly more energy in Arizona than in Alaska simply because Arizona gets more sunlight per day.
The level of sun exposure varies throughout the country. The following table outlines how many peak sun hours different regions of the United States get per month:
Region | Average monthly peak sun hours |
|---|---|
Northeast | 122 - 149 |
Southeast | 152 - 179 |
Midwest | 122 - 152 |
Northwest | 152 - 198 |
Southwest | 198 - 228 |
3. What solar panels will I use?
A solar panel’s wattage and efficiency will impact how many solar panels you need. Higher wattage panels with high efficiency ratings can generate more electricity than competitors. Keep in mind that the best solar panels tend to cost more money because of their increased performance.
4. How much solar can I afford?
Installing solar is a big investment, and the decision shouldn’t be taken lightly. Even though solar panels can provide thousands of dollars in electricity bill savings, the upfront costs might be too much. Take a look at your budget with a financial advisor and see if it’s actually affordable for you. If it seems like too much, you can consider installing fewer solar panels or different solar financing options.
5. What are my utility’s solar requirements?
You want to make sure you can meet all of your utilities requirements when installing a solar system. Does your utility limit how many solar panels you can install? Is there special interconnection paperwork you need to do? Does your utility require significant infrastructure upgrades to connect your solar panel system to the grid? Local solar installers will be familiar with the utility’s requirements in your area.
6. Do I have access to solar net metering?
Net metering, the process of sending excess solar energy to the grid in exchange for bill credits, is how solar panels save the most money possible. If your utility doesn’t offer full-retail net metering, you may want to consider installing fewer solar panels that only cover your day time electricity usage, or pairing the solar panels with a solar battery.
7. What is the condition of my roof?
Solar panels weigh about 40 pounds each, which can be a concern for older roofs. Have your roof system inspected to determine if your roof is suitable for solar panels and if it can handle the additional weight. Generally, this isn’t a concern for most homeowners. You also want to make sure that your roof won’t need to be replaced within the lifespan of the solar system, otherwise you’ll have to pay to remove each solar panel and have them reinstalled.
Can solar panels run an entire house?
Yes, solar panels can power your entire house, but it might not be in the way you think.
For most home solar arrays, solar panels only run your house during the day, and any excess solar energy produced is sent to the utility grid in exchange for electric bill credits through a process called net metering. Those credits are then used to cover all or a portion of the costs of electricity you use from the grid when your solar panels don’t produce energy, like at night.
If you want to run your house entirely on solar power, install a solar battery that will store excess electricity generated during the day for you to use later rather than sending it to the grid for bill credits. Battery storage is required for off-grid solar systems, as they don’t have the utility to fall back on.
Usually, a solar installer will install enough solar panels to generate your daily electricity usage during daylight hours, so you have credits to offset your electricity costs later. Solar companies use advanced software to provide accurate quotes that include the exact number of solar panels to meet your energy needs.
Catherine has been researching and reporting on the solar industry for five years and is the Written Content Manager at SolarReviews. She leads a dynamic team in producing informative and engaging content on residential solar to help homeowners make informed decisions about investing in solar panels. Catherine’s expertise has garnered attention from leading industry publications, with her work being featured in Solar Today Magazine and Solar ...
Learn more about Catherine Lane